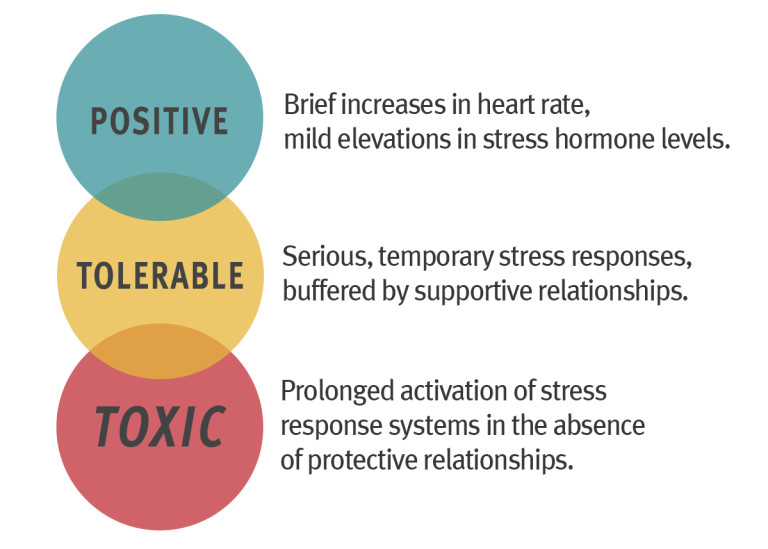
Understanding toxic stress and its impact on health and well-being

Stress is a normal part of our lives. It’s when we fail to process and manage this stress that it becomes harmful. There is good stress and bad stress, but it is all around us. Stress itself can be harnessed as a useful tool for motivation, it’s not all bad. But it’s when we have an abundance of unchecked stressors in our lives and ineffective coping mechanisms to deal with it that it becomes a problem.” That’s when therapy or counseling can make a big difference.
When a person experiences toxic stress, the prolonged activation of the body’s stress response begins to negatively impact the bod. Furthermore, stress increases your heart rate, creates elevated hormonal levels in your body, and causes higher blood pressure which can increase the risk of hypertension, heart attack and stroke. Additional physical and mental health conditions related to toxic stress include chronic fatigue, diabetes, obesity, depression and immune disorders.
Symptoms
Chronic stress affects both the mind and body. It produces both physical and psychological symptoms that can take a toll on a person’s ability to function normally in their daily life.
These symptoms can vary in their severity from one person to the next. Some of the most common signs of chronic stress include:
- Aches and pains
- Decreased energy
- Difficulty sleeping
- Disorganized thinking
- Fatigue
- Feeling a loss of control
- Feelings of helplessness
- Frequent illnesses and infections
- Gastrointestinal complaints
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Nervousness and anxiety
- Trouble concentrating
- Upset stomach
Identifying Chronic Stress
It isn’t always easy to recognize chronic stress. Because it is pervasive and long-lasting, people often grow so accustomed to it that it begins to feel normal. Some signs to look for when identifying chronic stress:
- Are you often moody or irritated?
- Does it feel like you are always worrying about something?
- Does it seem like you don’t have time to take care of yourself or do the things that you enjoy?
- Do the smallest inconveniences seem like too much to handle?
- Do you always seem to catch colds or get infections?
- Have you been relying on unhealthy coping mechanisms like alcohol to manage your stress?
How can therapy help with stress management? A therapist can work with you to understand major stressors, confront emotions, and identify helpful coping mechanisms.
1. Bring awareness to the major stressors in your life.
If you’re considering working with a counselor or therapist for stress management, you can expect them to help you identify the major stressors in your life. “Therapy can bring about awareness of what is actually causing an individual stress,” Stevon Lewis, Licensed Marriage and Family Therapist, explains. “Oftentimes, we aren’t aware of what is creating feelings of stress and making us feel overwhelmed. Talk therapy can assist with identifying stressors and singling out which is causing you the most distress.” He gives an example: “Sometimes we are stressed because we can’t or won’t say “no”. As a result, we take on too much and neglect ourselves. Therapy can help a person work through why they feel the need to say “yes” to everything and implement more appropriate boundaries that allow for them to place some priority over their own needs.”
Toxic Stress: Symptoms, Effects, Stress-Relief Tips (verywellmind.com)
Stress and Heart Health | American Heart Association
Both comments and pings are currently closed.